Stable Fly
Stomoxys calcitrans
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Diptera
- Superfamily: Muscoidea
- Family: Muscidae
- Subfamily: Muscinae
- Tribe: Stomoxyini
- Genus: Stomoxys
- Species: calcitrans
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Stomoxys calcitrans: /stɔˈmɔksɪs ˈkælsɪtrænz/
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
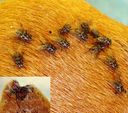
Stomoxys calcitrans, commonly known as the stable fly, is a blood-sucking fly that resembles houseflies but has distinct features. It feeds on the blood of livestock and can negatively impact cattle health and farming economics. It is also important for its role as a vector of several diseases.
Physical Characteristics
Adults are 5-7 mm long, closely resembling the common housefly but with a broader abdomen and characterized by four longitudinal stripes across the thorax and several dark dorsal spots on the abdomen. The proboscis is black, long, and thin. Larvae have uniquely shaped triangular, widely spaced spiracles.
Identification Tips
Look for the broader abdomen and distinct four longitudinal stripes across the thorax to differentiate from the common housefly.
Habitat
Abundant in and around areas where cattle are kept, larvae are found in rotting manure and decaying organic materials.
Distribution
Native to Eurasia and Africa, introduced into the New World during colonial times. Now found worldwide.
Diet
Adults feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals, primarily cattle and horses, during the daytime. Larvae feed on decaying organic matter and fecal materials.
Life Cycle
Life cycle duration is about two weeks at temperatures around 27 °C (81 °F), with the egg stage lasting 1-4 days and larvae lasting 11-30+ days before pupation for 6-20 days.
Reproduction
Females require engorged blood for egg production, laying eggs among putrefying organic materials. Males generally die after mating, and females die after laying eggs.
Ecosystem Role
Potential vector for various parasites and diseases.
Economic Impact
Cattle heavily infested may become anemic, and milking cows may show lower milk production. Known vector for several diseases.
Health Concerns
Considered a vector for Trypanosoma evansi, Trypanosoma brucei, brucellosis, equine infectious anemia, African horse sickness, fowlpox, and Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax.
Similar Taxa
Misconceptions
Often confused with the common housefly due to physical similarities but has different feeding habits.
Tags
- Stable Fly
- Cattle Fly
- Insect
- Vector
- Parasite