Stomoxys
Stomoxys
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Diptera
- Superfamily: Muscoidea
- Family: Muscidae
- Subfamily: Muscinae
- Tribe: Stomoxyini
- Genus: Stomoxys
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Stomoxys: /stoʊˈmɒksɪs/
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
Stomoxys calcitrans, also known as the stable fly, is a blood-feeding fly that impacts livestock health and agricultural production due to its feeding habits and role as a disease vector.
Physical Characteristics
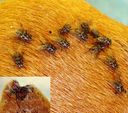
Adults are generally about 6–8 mm (1⁄4–5⁄16 inch) in length with a lighter color than the housefly, and a slightly wider and spotted abdomen. The mouth parts have biting structures unlike the sponging mouth parts of houseflies.
Identification Tips
Resembles the common housefly but is smaller and has a more robust body with a spotted abdomen.
Habitat
Abundant in and around where cattle are kept. Maggots are often found in rotting manure near cattle and poultry.
Distribution
Cosmopolitan; originally considered of Eurasian origin, now found worldwide.
Diet
Adults feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals.
Life Cycle
The life cycle duration is about two weeks at temperatures around 27 °C (81 °F), highly dependent on temperature and nutrient quality available for larvae.
Reproduction
Females require blood to engorge for egg production. Eggs are laid in putrefying organic materials such as hay, manure, and wood.
Ecosystem Role
Stable flies can affect the health of livestock and may impact animal agriculture operations due to blood feeding.
Economic Impact
Cattle heavily infested experience anemia and decreased milk production. This species is also considered a vector for several diseases in animals and humans.
Health Concerns
Potential vector of several pathogens including Trypanosoma evansi, Trypanosoma brucei, brucellosis, equine infectious anemia, African horse sickness, fowlpox, and Bacillus anthracis.
Collecting Methods
- Sweep netting
- Sticky traps
Preservation Methods
- Ethanol
- Pinned specimens
Evolution
The genus is stated to be a paraphyletic group based on data from Dsouli et al. (2011).
Similar Taxa
Misconceptions
Often confused with houseflies due to visual similarities, though there are significant differences in feeding behavior and mouthpart structure.
Tags
- Stomoxys
- Stable fly
- Muscidae
- Ecosystem impact
- Vectors