Soybean Aphid
Aphis glycines
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Suborder: Sternorrhyncha
- Superfamily: Aphidoidea
- Family: Aphididae
- Subfamily: Aphidinae
- Tribe: Aphidini
- Subtribe: Aphidina
- Genus: Aphis
- Species: glycines
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Aphis glycines: //ˈeɪfɪs ˈɡlaɪsiːniːz//
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
Aphis glycines, commonly known as the soybean aphid, is a significant pest of soybean in North America, originally from East Asia, that causes substantial agricultural damage through phloem feeding and indirect effects like viral transmission.
Physical Characteristics
<2 mm in size; green to yellow-green; often forms colonies on leaves of host plants.
Identification Tips
Look for small, green or yellow-green aphids clustered on soybean plants, especially on the underside of leaves.
Habitat
Soybean fields, particularly near populations of buckthorn (Rhamnus spp.) which serves as the primary overwintering host.
Distribution
Native to East Asia; introduced to North America in the 1990s; widespread across the eastern United States, especially in the Midwest.
Diet
Phloem sap from host plants, primarily soybean (Glycine max).
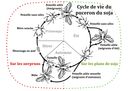
Life Cycle
Heteroecious holocyclic, alternating between primary host (buckthorn, Rhamnus spp.) and secondary host (soybean); undergoes sexual reproduction on primary hosts and parthenogenetic reproduction on secondary hosts.
Reproduction
Overwinters as eggs on buckthorn; in spring, eggs hatch into fundatrices that reproduce parthenogenetically; produces both winged (alate) and wingless (apterous) forms.
Predators
Natural enemies include ladybeetles, lacewings, pirate bugs, predatory flies, and entomopathogenic fungi.
Ecosystem Role
Acts as a key herbivore affecting soybean crop yields; serves as a food source for natural predators.
Economic Impact
Major pest of soybean; can cause yield loss of 50 to 70% in severe infestations.
Evolution
Part of the Aphididae family, known for its complex life cycles and host plant specificity.
Misconceptions
Sometimes mistaken for other aphids; its small size and color can be confused with non-pest species.
Tags
- Pest
- Agriculture
- Soybean