Dendroctonus brevicomis
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Suborder: Polyphaga
- Superfamily: Curculionoidea
- Family: Curculionidae
- Subfamily: Scolytinae
- Tribe: Hylurgini
- Genus: Dendroctonus
- Species: brevicomis
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Dendroctonus brevicomis: /dɛnˈdrɒktənəs brɛˈvɪkəmɪs/
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images




Summary
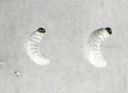
Dendroctonus brevicomis, the western pine beetle, is a significant pest of pine trees in North America, known for its role in tree mortality and its influence on forest fire dynamics.
Physical Characteristics
Adult D. brevicomis are brown or black beetles measuring 3–5 mm in length.
Identification Tips
Females carve lengthy egg galleries in the wood which is a sign of infestation.
Habitat
Dendroctonus brevicomis is typically found in forests dominated by ponderosa and Coulter pine trees.
Distribution
North America and parts of Mexico.
Diet
Feeds on the bark of pine trees, primarily ponderosa and Coulter pines.
Life Cycle
Females settle on the bark and attract males through pheromones for mating; they then lay eggs in galleries carved in the wood.
Reproduction
The female can control the sex ratio of the offspring by varying the proportions of pheromones she releases.
Ecosystem Role
As a bark beetle, it plays a role in the decomposition of dead trees and can trigger forest fires when tree mortality is high.
Economic Impact
D. brevicomis is known as a destructive pest that can lead to the death of significant numbers of pine trees, particularly during drought conditions.
Misconceptions
Some may believe all bark beetles are harmful, but they can play important ecological roles.
Tags
- Dendroctonus brevicomis
- western pine beetle
- Curculionidae
- bark beetle
- pine pest