Grape Phylloxera
Daktulosphaira vitifoliae
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Suborder: Sternorrhyncha
- Superfamily: Phylloxeroidea
- Family: Phylloxeridae
- Genus: Daktulosphaira
- Species: vitifoliae
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Daktulosphaira vitifoliae: //dæktjʊloʊˈsfaɪrə ˌvɪtɪˈfoʊli.iː//
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
Daktulosphaira vitifoliae, commonly known as grape phylloxera, is a serious pest of grapevines that affects their roots and leaves, leading to significant crop damage and economic loss. Native to eastern North America, it has spread worldwide and poses unique challenges in viticulture.
Physical Characteristics
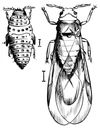
Adults are winged or wingless crawlers, oval or pear-shaped, and are almost microscopic, pale yellow sap-sucking insects.
Identification Tips
The majority of grape phylloxera adults are wingless females. Look for galls on grapevine leaves or deformations on roots.
Habitat
Found on the roots and leaves of grapevines, particularly on species of Vitis.
Distribution
Originally native to eastern North America and a serious pest of grapevines worldwide.
Diet
Sap-sucking insect that feeds on the roots and leaves of grapevines.
Life Cycle
Phylloxera has a complex life cycle consisting of up to 18 stages, including sexual form, leaf form, root form, and winged form.
Reproduction
Reproduces both sexually and parthenogenetically, with the female laying eggs in galls on leaves or on roots after mating with males.
Ecosystem Role
Most significant pest affecting grapevines, impacting viticulture globally and altering ecosystems involved.
Economic Impact
Significantly impacted grapevine production, particularly in Europe, leading to historical economic downturns in the wine industry.
Cultural Significance
Grape phylloxera has shaped grape cultivation practices and vineyard management, including the popularization of grafting onto resistant rootstocks.
Evolution
Phylloxera has evolved resistance mechanisms within its various strains and has proven highly adaptable.
Similar Taxa
Misconceptions
Some believe chemical controls or treatments exist; however, effective control largely relies on resistant rootstock grafting.
Tags
- pest
- vineyards
- grape
- Daktulosphaira vitifoliae
- agriculture
- hemiptera