Daktulosphaira
Daktulosphaira
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Suborder: Sternorrhyncha
- Superfamily: Phylloxeroidea
- Family: Phylloxeridae
- Genus: Daktulosphaira
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Daktulosphaira: //ˌdæktjʊloʊˈsfaɪrə//
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
Grape phylloxera (Daktulosphaira vitifoliae) is a significant insect pest of grapevines that leads to severe economic impacts on vineyards and wine production worldwide, originally native to North America.
Physical Characteristics
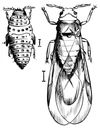
Almost microscopic, pale yellow sap-sucking insects.
Identification Tips
Look for galls on leaves and root deformations.
Habitat
Grapevine roots and leaves, particularly in vineyards.
Distribution
Originally native to eastern North America, found worldwide in grapevine regions.
Diet
Sap-sucking, primarily feeding on roots and leaves of grapevines.
Life Cycle
Complex life-cycle consisting of up to 18 stages divided into sexual form, leaf form, root form, and winged form.
Reproduction
Parthenogenetic reproduction occurs after mating; can reproduce several generations a year in suitable conditions.
Ecosystem Role
Pest of grapevines, playing a role in vineyard ecosystem dynamics.
Economic Impact
Harmful pest causing significant decline in grapevine health and vineyard productivity, affecting wine production.
Cultural Significance
Significant historical impact on European viticulture, leading to changes in grape farming practices.
Collecting Methods
- Trapping with sticky traps
Preservation Methods
- Preservation in alcohol for future study
- Frozen storage for genetic research
Evolution
Well-adapted to various climates and hosts due to its complex reproductive strategy.
Similar Taxa
- Aphids
- Other phylloxerids
Misconceptions
Not a disease but a pest; control methods vary with grape type and region.
Tags
- insect
- grape pest
- phylloxeridae
- Daktulosphaira
- grapevine
- vineyards