Hairy Rove Beetle
Creophilus maxillosus
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Hexapoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Suborder: Polyphaga
- Superfamily: Staphylinoidea
- Family: Staphylinidae
- Subfamily: Staphylininae
- Tribe: Staphylinini
- Subtribe: Staphylinina
- Genus: Creophilus
- Species: maxillosus
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Creophilus maxillosus: /ˌkriːoʊˈfaɪləs ˌmæksɪˈloʊsəs/
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
Creophilus maxillosus, or the hairy rove beetle, is a predacious species found in wooded habitats, primarily feeding on decomposing carrion and maggots. It plays a crucial role in the ecosystem as a scavenger and predator and is often used in forensic investigations related to decomposition.
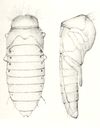
Physical Characteristics
Adults are shiny black, 12–18 mm long with large eyes and needle-like jaws. Larvae are cylindrical and stout, measuring 20–25 mm long. They have golden setae on various body parts including the head and elytra.
Identification Tips
Look for large eyes, thick beaded antennae with 11 segments, and the unique ability to form a tight ball when disturbed. The elytra cover the first few abdominal segments.
Habitat
Found in grassy and open forested habitats, along lake/ocean shorelines, and areas with carrion. They are often located in forest leaf litter and decaying plant material.
Distribution
Native to North America and the Palaearctic. In North America, it is widespread in the eastern U.S. and recorded from regions such as Ontario, Quebec, and Massachusetts.
Diet
Predacious, feeding on carcasses and maggots from decaying animals. Both larvae and adults have long mandibles adapted for chewing.
Life Cycle
Eggs develop in around 4 days, larvae last about 14 days, and pupae for 16 days, with a total life cycle duration estimated at 37 days.
Reproduction
Adulthood is typically marked by the laying of eggs in fresh sand. The specifics of mating behavior are not detailed.
Predators
Commonly preyed upon by various insectivorous animals, including larger predatory insects.
Ecosystem Role
Plays a significant role as a scavenger and predator in decomposition processes. Known to impact populations of Diptera larvae at carrion sites.
Economic Impact
Considered beneficial due to its role in scavenging and controlling maggot populations, though it may infest houses.
Health Concerns
Can inflict a painful bite with its mandibles if handled carelessly.
Collecting Methods
- Hand collection in wooded areas
- Using pitfall traps near carrion
Preservation Methods
- Ethanol preservation
- Pinning for adult specimens
Similar Taxa
Misconceptions
Some may confuse C. maxillosus with other beetles due to its shiny appearance and habitat, not realizing its predatory behavior and specificity to carrion.
Tags
- Rove Beetle
- Predatory Insect
- Forensic Entomology
- Decomposition
- Carrion Scavenger