Brine Shrimp and Fairy Shrimp
Anostraca
Classification
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Subphylum: Crustacea
- Class: Branchiopoda
- Order: Anostraca
Pronunciation
How to pronounce Anostraca: //æˈnɒstrəkə//
These audio files are automatically generated. While they are not always 100% accurate, they are a good starting point.
Images





Summary
Anostraca, known as fairy shrimp and brine shrimp, are small crustaceans found in various aquatic environments, renowned for their intriguing life cycles that include the ability to enter diapause as durable eggs. They serve as important food for birds and fish and are cultivated for aquaculture.
Physical Characteristics
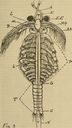
Typically 6–25 mm (0.24–0.98 in) long, with some species growing up to 170 mm (6.7 in). Body is elongated, divided into segments, with thin flexible exoskeleton and no carapace. Head bears compound eyes and two pairs of antennae. Thorax has 13 segments with leaf-like phyllopodia, and abdomen consists of 6 segments plus telson with cercopods.
Identification Tips
Look for elongated body lacking a carapace and possessing 11 pairs of phyllopodia. Notable species like the giant fairy shrimp (Branchinecta gigas) can be identified by size and specific anatomical features.
Habitat
Vernal pools, hypersaline lakes, deserts, ice-covered mountain lakes, Antarctic ice, and other ephemeral water bodies.
Distribution
Found worldwide, with some species in extreme environments including Antarctica and high altitudes. Anostraca are distributed across all seven continents.
Diet
Filter feeders, consuming organic particles from water and scraping algae from surfaces; some species, like Branchinecta gigas, are predatory.
Life Cycle
Life cycle includes a universal ability to enter diapause as eggs, which can withstand extreme environmental conditions and remain viable for centuries.
Reproduction
Most species are gonochoristic (separate sexes), but some reproduce by parthenogenesis. Reproductive appendages are specialized in males for mating.
Predators
Predatory fish and birds, with higher vulnerability in areas with greater predator presence.
Ecosystem Role
Serve as a significant food source for various aquatic birds and fish, also play a role in the ecosystem of ephemeral freshwater habitats.
Economic Impact
Cultured for use as fish food in aquaculture; the industry centered around brine shrimp is a multimillion-dollar market.
Collecting Methods
- Surface collection from ephemeral and saline bodies of water.
- Drawing water samples to collect eggs and larvae.
Preservation Methods
- Dry storage of eggs for transportation and later hatching.
- Freezing of adults for later use.
Evolution
Believed to have diverged from other Branchiopoda during the Ordovician period, showing adaptations to escape predation in marine environments.
Misconceptions
Often considered insignificant; however, they play an important role in their ecosystems as food sources and indicators of environmental changes.
Tags
- Anostraca
- fairy shrimp
- brine shrimp
- crustaceans
- Branchiopoda